We are going to present you workflow that shows how a YouTube video is downloaded to a subscriber device via Google Global Caches installed in LG U+. Below, we will look at downloading over the KT Internet, which has no Google Global Cache installed in it.
In the subsequent post, downloading procedures in the LG U+ Internet, which has Google Global Caches installed in it, will be discussed using two different cases - on a Cache Hit and on a Cache Miss (i.e. when a Google Global Cache has a video requested and when it does not).
YouTube Downloads over the KT Network
We assumed a network configured as follows for the purposes of this post:
- On the grey board in the left [Google Server (USA)]: YouTube server (www.youtube.com) and Google Global Cache (o-o.preferred.lax04t01.v1.lscache6.c.youtube.com) located in US
- On the grey board in the right [KT Network (Korea)]: A KT subscriber connected to KT network in Korea
- On the grey board in the middle [Transit]: Transit network that connects KT network to a network in US
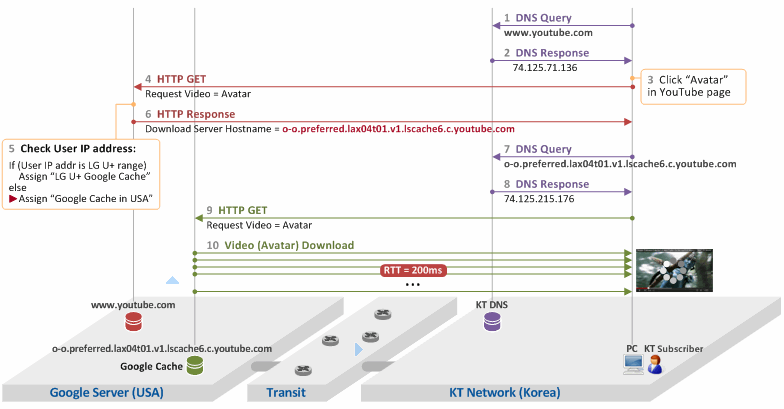
- The KT subscriber enters www.youtube.com into his browser to access a YouTube server. The subscriber device sends a DNS query to a KT DNS server (the DNS server doesn't have to be a KT DNS server) to obtain the IP address of the YouTube server.
- The KT DNS server gives the subscriber device the IP address of the YouTube server (i.e. 74.125.71.136).
- The subscriber accesses the YouTube server and clicks "Avatar" on YouTube.
- The subscriber device sends a HTTP GET message to the YouTube server to request an Avatar video.
- This is the most important step of the process. The YouTube server checks the IP address of the subscriber device when it receives the HTTP GET message. This step is to check whether or not the IP address of a device is within the range assigned to an operator who has Google Global Caches installed in its network. In this example, KT has no Google Global Cache in its network.
- Therefore, the YouTube server gives the hostname of a Google Global Cache located in US (i.e. o-o.preferred.lax04t01.v1.lscache6.c.youtube.com) to the subscriber device.
- The subscriber device performs a DNS query about hostname = o-o.preferred.lax04t01.v1.lscache6.c.youtube.com.
- As a result of the query, the subscriber device receives an IP address of 74.125.215.176, which is the IP address of the Google Global Cache located in US.
- Now, the subscriber device sends a request for the video to the server at 74.125.215.176.
- The subscriber downloads the video from the Google Global Cache (presumably located in LA since the hostname has "lax"). The RTT between two countries is very high - about 200 ms. Besides, if there is heavy traffic (e.g. in the evening), buffering will be severe. Severe enough to keep the subscriber from watching the video.

how to connectl GGC servers to its own Network and what is the implementaion procedure means which N/W elements is reuired? how give the coonectivity for switch to router?
Hi Nidhi,
I hope help you with the following document:
https://www.netmanias.com/ko/?m=view&id=cshare&no=5455